Il pensiero critico ti permette di prendere decisioni migliori. Consiste in processi mentali basati sulla capacità di giudicare bene, analizzare e valutare. Comprende possibili processi di riflessione al fine di formare un giudizio solido che concili l'evidenza con il buon senso. Il pensiero critico implica chiaramente la sintesi, la valutazione e la ricostruzione del pensiero, oltre all'analisi. I pensatori critici raccolgono informazioni da tutti i sensi, espressioni verbali e/o scritte, riflessioni, osservazioni, esperienze e ragionamenti. Il pensiero critico ha le sue basi in criteri intellettuali che vanno oltre le divisioni tematiche e che includono: chiarezza, credibilità, accuratezza, precisione, pertinenza, profondità, ampiezza, logica, significato e correttezza.
Pensare in modo critico significa non essere ciechi ed accettare tutte le conoscenze acquisite, ma saperle valutare adeguatamente. Qualcosa è vero o buono solo perché la maggior parte crede che sia vero o buono? Il pensiero critico è la ricerca di una verità più profonda. Il pensatore critico chiede: "È vero?" Il pensiero critico è la ricerca di ragioni più profonde per determinate azioni. Si riferisce a una delle competenze di base per tutta la vita: imparare a pensare.
Il pensiero critico e l'apprendimento sono una delle attività più importanti nell'età adulta. Durante questo periodo, il pensiero critico è connesso con tutta la nostra vita, con l'intero spettro delle diverse aree in cui dimostriamo il pensiero critico con originalità, intransigenza e capacità di trovare nuove alternative.
Spesso associamo o confondiamo il pensiero critico con il pensiero logico, creativo o laterale. Tuttavia, il processo di pensiero critico è diverso da quelli elencati. Contiene molte componenti, comprese quelle mentali ed emotive, che, ad esempio, lo separano in modo significativo dal pensiero logico.
Soprattutto, lo scopo del pensiero critico è importante in questo: stiamo cercando di vedere che il nostro pensare, agire o comportarci finora (o interagire e comportarci con gli altri) non è necessariamente l'unico corretto o addirittura il più appropriato. Attraverso il giudizio critico, scopriamo nuove alternative, tra cui poi scegliamo l'opzione più appropriata per noi, a seconda degli obiettivi che vogliamo raggiungere.
In generale, possiamo parlare di due tipi di pensiero:
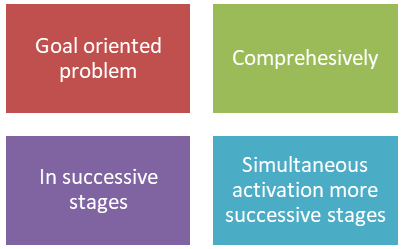
Il pensiero convergente è caratterizzato dalla verticalità del pensiero, il cui fondamento è l'integrità e l'orientamento all'obiettivo, di solito partendo da diverse opzioni fino ad arrivare all'unica soluzione corretta.
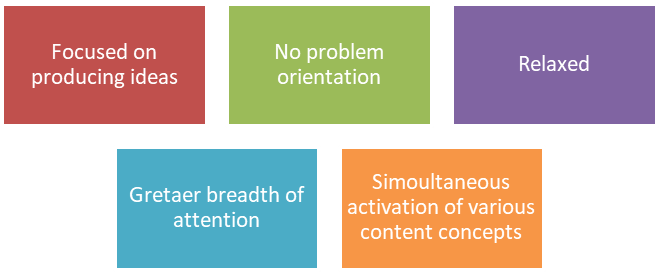
Il pensiero divergente, d'altra parte, equiparato al pensiero creativo, è caratterizzato dalla flessibilità e dalla presenza di una moltitudine di idee in un breve lasso di tempo. Tale pensiero è laterale o orizzontale, si potrebbe dire che sia innescato in modo consapevole e deliberato dal pensiero intuitivo.
Come scopriamo che questo è un pensiero critico? Quali processi sono in atto allora?
1. Il pensiero critico è un'attività produttiva e positiva
Quando pensiamo in modo critico, percepiamo comportamenti, valori, strutture sociali e altre forme di accadimento diverse, pur essendo consapevoli che anche le altre persone sono convinte della correttezza delle loro azioni e del loro modo di pensare.
2. Il pensiero critico è un processo, non un risultato
Il pensiero critico è una continua messa in discussione delle previsioni; dubitiamo sempre, anche se abbiamo raggiunto il livello più alto di pensiero critico.
3. Il verificarsi del pensiero critico dipende dalle circostanze in cui si svolge
Il pensiero critico emerge principalmente come pensiero (espresso per iscritto o oralmente) o come azione concreta che ha esiti diversi nell'ambiente.
4. Il pensiero critico può essere innescato da eventi positivi e negativi
L'opinione prevalente è spesso che il pensiero critico sia il risultato di eventi traumatici o tragici che sperimentiamo, e così facendo mettiamo in dubbio la correttezza del nostro pensiero precedente. È vero che tali eventi sono più spesso motivo di riflessione, ma è proprio lo sviluppo del pensiero critico che ci consente di ridurre il numero di tali casi.
Tuttavia, il pensiero critico è innescato anche da eventi piacevoli, durante i quali ci si interroga anche sull'adeguatezza delle nostre precedenti esibizioni.
5. Il pensiero critico è emotivo e razionale
Sebbene il pensiero critico possa essere inteso come un processo strettamente razionale, le emozioni sono in realtà essenziali in esso. Vale a dire, spesso iniziamo a risolvere i problemi in modo diverso quando accade qualcosa che ci rende tristi, arrabbiati, gioiosi, risentiti e così via.
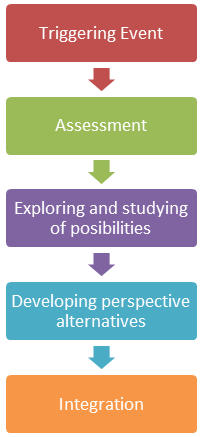
Il processo di pensiero critico avviene sempre attraverso fasi, fasi che portano l'individuo al risultato finale: un cambiamento nel comportamento, nel pensiero o in qualche altra decisione.
Le fasi del pensiero critico possono essere chiamate in modo diverso, ma corrispondono per lo più alle stesse attività. Stephan Brookfield le ha chiamati come segue:
Caratteristiche dei pensatori critici
Il pensiero critico è importante in tutti i settori della nostra vita. Ci offre nuove prospettive su fenomeni già noti, solleva dubbi su verità generalmente accettate e apre nuove strade. Sulla base di ciò, possiamo dire che nell'odierna epoca di rapidi cambiamenti, è particolarmente importante anche relativamente a questioni di tipo socio-politico.
Pensando in modo critico, esaminando tutti i lati di un problema, evento o circostanze, riflettendo sulle esperienze passate e ascoltando ciò che il cliente (utente) o altri membri del gruppo hanno da dire, potresti arrivare a una svolta che fa avanzare il tuo sviluppo personale in modi nuovi ed entusiasmanti. Il pensiero critico è un'abilità della persona importante e necessaria nel volontariato in tempi di crisi.